- Solutions
- Case studies
- Company
- Career
Susceptors (alternatively also known as muffles) are the heart of every heat treatment system and are usually made of robust graphite
and CFC
. They ensure a homogeneous temperature distribution in the working chamber and thus enable precise, reproducible and energy-efficient heat treatment processes. As large forces act on the areas of the furnace opening when loading and unloading heavy workpieces, they must not only be heat-resistant, but also extremely mechanically resilient. Read here how Graphite Materials has met this challenge.
Share case study
Industry:
Tool, mold and machine construction
Procedure:
Heat treatment
Solution:
Services:
Consulting, engineering technical documentation, manufacturing
Result:
– Increased service life – Reduced exchange frequency – Reliable load capacity in the loading area |
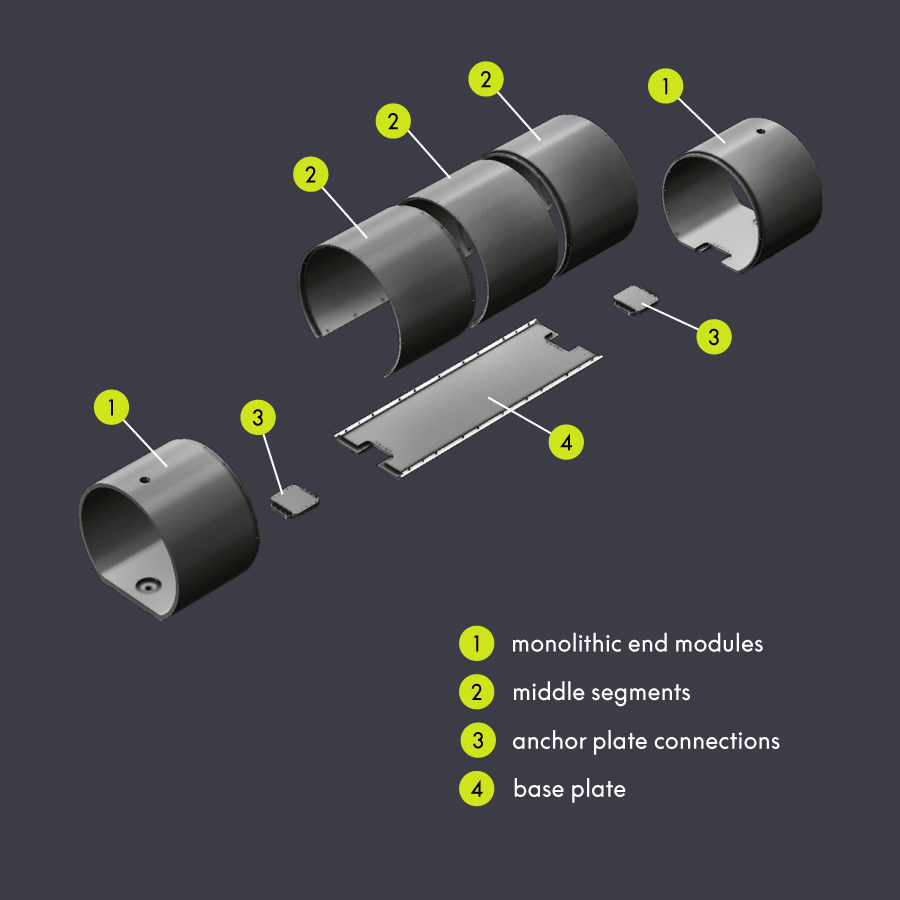
Conventional susceptors consist of several assembled modules, usually in two parts: a flat base element and a circular segment above it. However, this design has a decisive disadvantage: the mechanical weakness at the loading opening.
The regular insertion and removal of heavy workpieces using a roller system (e.g. carbide blanks) creates large forces, particularly on the first base element. These can lead to cracks or fractures in modular designs, with considerable consequences for production, maintenance and cost-effectiveness.
The aim was to develop a new graphite muffle that could withstand high thermal and mechanical requirements without structural weaknesses at the joints in the loading zone. The requirements of the new design were: